三分,是一个建立在分治基础上的一个算法,目的是求单峰函数上的极值。
单峰函数
单峰函数是一个凹函数或一个凸函数,设它的峰值是 ,则它在 上单调递增(或单调递减),在 上单调递减(或单调递增)。
例如,这是一个单峰函数:
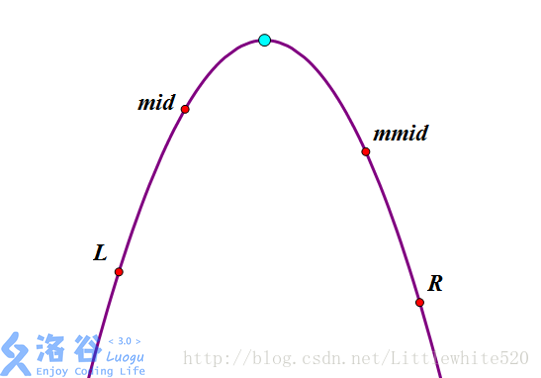
我们先取 的中点 ,再取 的中点 ,通过比较 与 的大小来缩小范围。
不难发现以下性质:
-
当
一定在白点的右边。
反证法:假设 在白点的左边,则 也一定在白点的左边,又由 可推出 ,与已知矛盾,故假设不成立。 所以,此时可以将 来缩小范围。
-
一定在白点的左边。
反证法:假设 在白点的右边,则 也一定在白点的右边,又由 可推出 ,与已知矛盾,故假设不成立。
若图像是个凹函数,则把性质反过来就是了。
模板
整数
int three_devide(int l,int r) //找凸点
{
while(l<r-1)
{
int mid=(l+r)/2;
int mmid=(mid+r)/2;
if(f(mid)>f(mmid))
r=mmid;
else
l=mid;
}
return f(l)>f(r)?l:r;
} 小数
double three_devide(double low,double up)
{
double m1,m2;
while(up-low>=eps)
{
m1=low+(up-low)/3;
m2=up-(up-low)/3;
if(f(m1)<=f(m2))
low=m1;
else
up=m2;
}
return (m1+m2)/2;
} 例题
#include<stdio.h>
int n;
double l,r,eps=0.000005,x[21];
double power(double a,int b)
{
double ans=1;
for(int i=1;i<=b;i++)
ans*=a;
return ans;
}
double count(double a)
{
double ans=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n+1;i++)
ans=ans+x[i]*power(a,n-i+1);
return ans;
}
double three_devide(double low,double up)
{
double mid,mmid;
while(up-low>=eps)
{
mid=low+(up-low)/3;
mmid=up-(up-low)/3;
if(count(mid)>count(mmid))
up=mmid;
else
low=mid;
}
return up;
}
int main()
{
int i;
scanf("%d%lf%lf",&n,&l,&r);
for(i=1;i<=n+1;i++)
scanf("%lf",&x[i]);
printf("%.5lf",three_devide(l,r));
return 0;
}
